
Raedle, J. (2022, Nov. 6). Trump Wearing a MAGA hat. [Photograph]. NBC. https://www.nbcnews.com/meet-the-press/meetthepressblog/numbers-trump-backed-candidates-fared-midterms-rcna61524
“In Springfield, they’re eating the dogs. The people that came in, they’re eating the cats. They’re eating—they’re eating the pets of the people that live there” says Donald Trump, the president of United States (Rushton, 2025).
This hate speech aims to target Haitian immigrants. Hate speech, is defined as speech that incites people to look down on certain social group (Flew, 2021, p.115).
It happens in the middle of the US presidential debate (Thomas and Wendling, 2024). It is shocking to see that a presidential candidate could say something that is so racism and baseless just to win votes. It all started from a Facebook post, see below:

Liddell. (2024, Friday 13). Facebook post spreads hate speech on Haitian immigrants.
[Screenshot]. Indepedent News. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/us-politics/trump-haitian-eating-pets-immigrants-facebook-source-b2612208.html
The person who posted, according to Independent News, is called Erika Lee. She admitted to the journalists that she heard this story from a neighbor, but her neighbor heard it from a friend, and this friend heard it from their daughter (Liddell, 2024). BBC News verified with the local officials and was told that there are no report or any kind of claim that could indicate that immigrants in Springfield had abused animals or other person’s pets. (Thomas and Wendling, 2024).
The BBC further noted that there are other similar claims of “missing animals” that emerge in the similar time period and in the same state (Ohio). For example, a Reddit post show a man carrying goose and they also attributed the missing goose to Haitian immigrants.
One of the tactics Trump’s “MAGA” movement is to target illegal immigrants. According to the Whitehouse FACT SHEET: President Donald J. Trump Protects the States and the American People by Closing the Border to Illegals via Proclamation (2025), Trump claim that “Illegal immigration affects the lives of all Americans” (The White House, 2025). He suggests that illegal immigrants takes away American’s jobs and they are bad for the economy. However, according to Aljazeera’s fact check report, most Haitian immigrants are legal immigrants. Journalist Maria Ramirez Uribe from Aljazeera indicate that although they cannot track on very immigrant’s status in Springfield, but the officials claim that most of them are legal immigrants who under legal protections (Uribe, 2024)
Thus, why are legal immigrants face same allegation as the illegal immigrants. Look at Trump’s use of words “The people that came in”, this seems to include all immigrants, whether they are legal or not.
ABC says that this baseless Springfield story went viral online thanks to the help from right-wing politicians and vice presidential nominee (now the vice president) Sen JD Vance (Reinstein and Demissie, 2024). Reinstein and Demissie (2024) reveal that there is a specific force behind spreading the hate.
The question this blog aims to examine is why misinformation and fake news could spread so widely on the internet. Is it because of our technology? For example, the rise of social media, the low entrance to post information and a large user base. Or structural? For example, the unequal structural of the society, or the institutional authorities such as Trump and Vance who actively participated in the process of spreading false information?
A Technical View:
Social media seems to be always the first thing to blame when we think of the misinformation and fake news. This might because most of our information came from social media, and therefore, we might think it is the place for misinformation and fake news.
However, as Livingston and Bennett (2020) reveals, blaming technologies does not explain why there is a huge demand for disinformation (p.5). Disinformation, is the intention to spread false information in order to achieve the purpose of manipulating public’s perceptions of something (Flew, 2021).
In this particular case of Haitian immigrants, social media may play a less determining role. Looking from a superficial level, it seems that social media such as Facebook and Twitter allow the message to spread more widely and thus, it should be subject to blame. The common approach is that we demand social media platform to censor fake and harmful information (Livingston and Bennett, 2020). However, Flew (2021) asks, should or can we trust platforms to censor these content?
The social media platforms are NOT innocent, their business model determines that they are not neutral. For example, Benkler et al. (2018) demonstrates how any person such as Trump’s campaign could pay Facebook and use Facebook’s deep data to promote their content (p.11). Thus, if fake news and disinformation are profitable for the social media platforms, they are less likely to moderate or flag the content that they were told to promote.
A famous scholar—Marshall McLuhan introduce the idea that “Medium is the message”. The idea suggests that all medium, such as social media in this case, shapes how we think about message (Kadavy, n.d). For example, Kadavy (n.d) comments on how social media allows fake news to share more easily. This concern is found in Flew’s (2021) chapter as well, as Flew (2021) suggests that the lower bar to entry social media may give birth to fake news (p.111) If we think about it, journalists posts tend to get reviewed before they can publish because their profession is at stake if they don’t follow professional rules, but for common people, we don’t have any constraints.
The data on anonymous users on Facebook is shocking:
Armstrong. (2020, Feb 3). 16% of All Facebook Accounts Are Fake or Duplicates. [Charts]. Statista. https://www.statista.com/chart/20685/duplicate-and-false-facebook-accounts/
As shown in this image from Statista (2020)by Armstrong, the percentage of Facebook fake accounts rise steadily year by year. We can guess that other social media platforms may face the same problem.
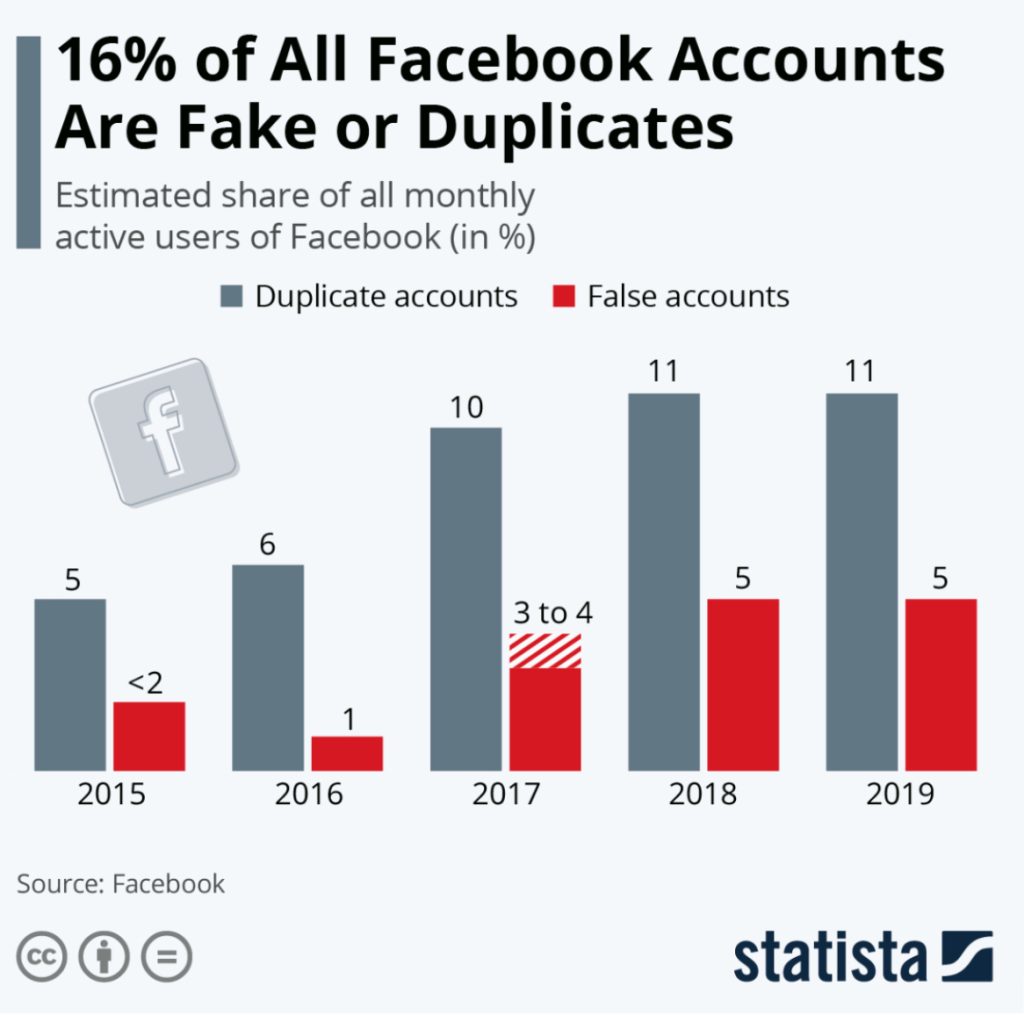
Therefore, there is a very low barrier to entry social media,
which made easier for people who may want to spread fake news.
What complicates the issue is that we also have large users who use social media as their main media source, for example, as Flew’s (2021) 2017 data shows (p.112), 51% US News Consumer use social media to access news. Moreover, the built in function in social media such as liking and share also makes fake news more easy to reach people (Flew, 2021, p.112)
To summarize, social media is not innocent in promoting fake news and disinformation. However, as Bennett and Livingstone (2020) reveals, currently social media takes most of the blame (p.5). When we focus on social media only, we may overlook other factors that interplayed in spreading the fake news and disinformation. Tools are essentially tools, it lacks human consciousness. Just because social media is made it more easier to spread fake information, it does not mean that the persons using the tool can escape from examination. Not to mention that fake information preceded the introduction of social media (Benkler et al., 2018, p.42).
A Structural View:
Livingston and Bennett (2020) stress that the origin of fake news is because authoritative institutions are rotten (p.4). The authors mention that in a “well functioning public sphere”, people would have trust in authoritative institutions because the institutions will present well-informed piece with a balanced perspectives (Livingston and Bennett, 2020, pp. 10-11).
However, now people’s trust in institutions has been broken, and such trust is not easy to restore (Livingston and Bennett, 2020). Therefore, people turn to alternative media might because they simply think the official source is biased and untrue. However, having alternative media does not increase democracy necessarily. As Livingston and Bennett (2020) shows, people have confirmation bias. They would tend to turn to media that confirms with their existing views.
Thus, alternative media may not be necessarily better than official institutional media if people only looking for news or perspective that makes them feel good. Moreover, alternative media could also be used to spread disinformation (Livingston and Bennett, 2020).
For example, Haitian immigrants disinformation started from common people’s post rather than official institutions. When people believe in these hearsay more than official institutions, they still cannot escape from fake information.
Therefore, Livingston and Bennett (2020) reveal that the malfunctioning public sphere is what we should be examining. The question is, what forces made the public sphere malfunction? We need to take a look at the history in order to understand the it. The following will be focusing on U.S history.
Ethics of Press Institutions
In the past, press institutions are very against to include conspiracies in their publication (Bennett and Livingstone, 2020, p.9). Right now, the liberal democratic institutions such as press are actively involved in bringing conspiracies. Additionally, currently, press institutions has their own political stance too. For example, Fox News takes on the conservative side Benkler et al., 2018, p. 52).
Neoliberalism
Neoliberalism perpetuates the idea that less government is better. Thus, there was a constant movement of undermining the government and authoritative figures (Livingston and Bennett, 2020, pp. 16-17). Therefore, the belief that government and politicians are bad implanted in people’s heart.
These two factors breaks people’s trust with officials or any institutions that is affiliated with government. There are other factors too, as revealed in Livingston and Bennett’s (2020) chapter. However, due to the limitation of the blog, it’s difficult to elaborate on all of them.
Therefore, a malfunction public sphere is a soil for fake news and disinformation. Multiple stakeholders fail to take on their responsibilities to maintain a functional public sphere. People turn to alternative media that could be biased just as the same, but they can chose to read what makes them feel good.
Additionally, as we saw in the case study presented above, Trump and his administrators are even actively promoting disinformation and hate speech for their own purposes. The media becomes their tool of getting what they wanted.
We really live in a “post-truth” era where it seems everything is fake.
A combined view:
It’s time for us to use a combined view to examine the spreading of disinformation and fake news, as well as hates speech. On the one hand, we have social media platforms that set the foundation for spreading message of any kind more widely and faster. The business model that social media platform has, makes it unlikely that we could rely on them to moderate or censor fake information. On the other hand, there are forces behind social media that lead to the prevalence of disinformation and fake news. On the public side, people turn to alternative media because they lost trust with the government. But alternative media also risk to be bias and spreading unchecked facts too. On the media side, spreading fake information is often to achieve their political purposes, and they have the means and resources to do so.
Concluding Thought
So, what we should do? It seems that it is impossible for individuals to develop a kind of media literacy that could navigate in this post truth world. How media literate can one be in order to see through hundreds and thousands of fake information that is constantly updated each day.
Regulation has to take place from top to bottom. The government should start to end using social media as means it to its end, and bring back press institutions that are critical. The social media platform should be regulated in terms of changing its business model, otherwise, fake information will continue to be promoted.
As individuals, we should see disinformation and fake news from a combined view. Not only we see how social media participated in disseminating fake information, but also how other forces are using social media. In the case of Trump against Haitian immigrants’ hate speech, if we can understand why Trump said that (eg. For MAGA), we are more likely to see it as unchecked facts. Perhaps the best we can do is to recognize there are unchecked facts, and do not believe them.
References:
Armstrong. (2020, Feb 3). 16% of All Facebook Accounts Are Fake or Duplicates. [Charts]. Statista. https://www.statista.com/chart/20685/duplicate-and-false-facebook-accounts/
Benkler, Y., Faris, R. & Roberts. H. (2018). Epistemic Crisis. In Network Propaganda:
Manipulation, Disinformation, and Radicalization. New York: Oxford University Press, (pp. 3-43).
Flew, T (2021). Disinformation and Fake News. In Regulating Platforms. Cambridge: Polity, (pp.
111-114).
Kadavy, D. (n.d). What does “the medium is the message” mean? Kadavy.Net.https://
kadavy.net/medium-is-the-message-meaning/
Livingston, S. & Bennett, W. L. (2020) A Brief History of the Disinformation Age: Information
Wars and the Decline of Institutional Authority. In S. Livingston & W. L Bennett (eds.) The Disinformation Age: Politics, Technology, and Disruptive Communication in the United States. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, (pp. 3-40).
Liddell, J. (2024, September 13). Origin of Trump and JD Vance’s lies about Haitian immigrants
eating pets revealed. Independent. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/us-politics/trump-haitian-eating-pets-immigrants-facebook-source-b2612208.html
Reinstein, J. & Demissie, H. (2024, September 11). Trump pushes false claim that Haitian migrants
are stealing and eating pets. ABC News. https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/trump-pushes-false-claim-haitian-migrants-stealing-eating/story?id=113570407
Rushton, G. (2025, March 16). How checking facts got political. ABC. https://www.abc.net.au/
news/2025-03-16/fact-checking-partisan-media-meta-trump-politics/105046680
The White House. (2025, Janurary 22nd). FACT SHEET: President Donald J. Trump Protects the
States and the American People by Closing the Border to Illegals via Proclamation. The White House.https://www.whitehouse.gov/fact-sheets/2025/01/fact-sheet-president-donald-j-trump-protects-the-states-and-the-american-people-by-closing-the-border-to-illegals-via-proclamation/
Thomas, M. & Wendling, M. (2024, September 16). Trump repeats baseless claim about Haitian immigrants
eating pets. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c77l28myezko
Uribe, R, M. (2024, October 5th). Fact check: Are Haitian immigrants in Springfield in the US illegally?

Be the first to comment